What Is GPT-5-Codex?
GPT-5-Codex is OpenAI’s latest specialized version of their GPT-5 model, optimized for “agentic coding”—that is, coding tasks where the model acts more autonomously, handling full workflows rather than only responding to prompt-by-prompt commands.
It’s tightly integrated into the OpenAI Codex ecosystem, including Codex CLI, Codex Cloud, the IDE extension, and tools for code review. It aims to serve both interactive sessions (small tasks, real-time developer collaboration) and long, complex tasks (large refactors, cross-repo work) with higher reliability.
Key Metrics & What Makes It Special
- SWE-bench Verified Benchmark: GPT-5-Codex achieved a 74.5% success rate on real-world coding tasks in the SWE-bench test suite.
- Refactoring Performance: It improved from ~33.9% (with generic GPT-5) to ~51.3% on large-scale refactor tasks.
- Token Efficiency on Lightweight Tasks: For small, clearly defined requests, GPT-5-Codex uses 93.7% fewer tokens compared to generic GPT-5. This means cost and latency improvements where tasks are small.
- Long-running Task Capability: In tests, it can operate independently for over seven hours, working through big refactors, resolving test failures, and producing successful final outputs.
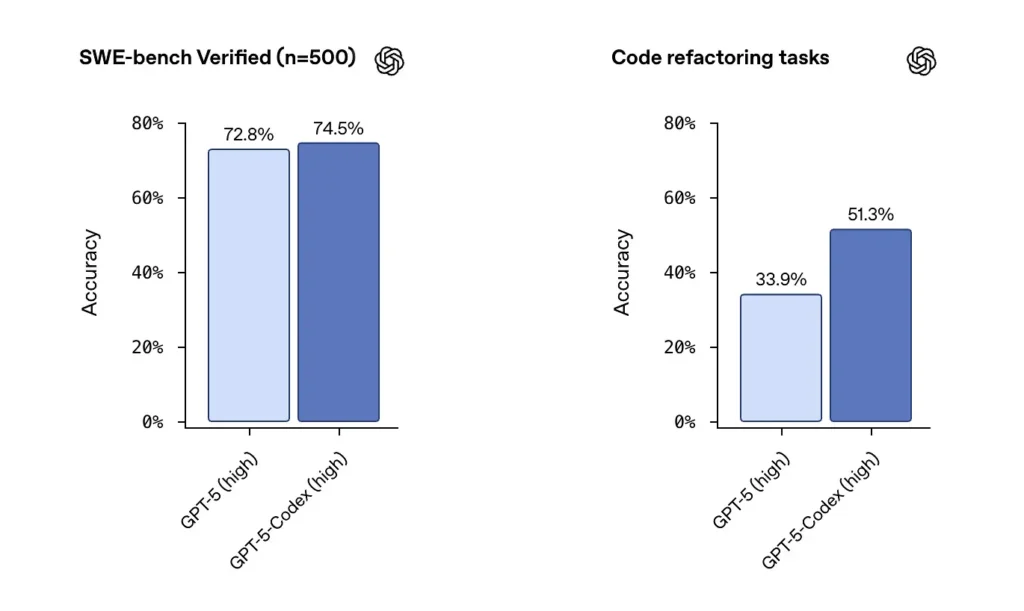

Image Source: openai
GPT-5-Codex: Purpose-Built for Developer Workflows
- As already noted, GPT-5-Codex is a variant of GPT-5 tailored for coding workflows. It is the default model for many Codex tasks (cloud tasks, code review) and is optionally selectable via CLI or IDE.
- The model is trained with a combination of agentic tools (where it’s given more autonomy), extended reasoning capacity, and abilities to test, refactor, and validate as part of its workflow.
Is Codex Better Than GPT?
Here “GPT” generally refers to generic GPT-5 (or prior versions) versus the coding-optimized GPT-5-Codex:
- On generic tasks (e.g., narrative generation, general conversation), standard GPT-5 may perform equally or better in certain criteria, especially when reasoning is needed outside the domain of software engineering. GPT-5-Codex, being specialized, may trade off some generality.
- But for coding, especially in complex or long tasks (refactors, cross-file work, test correction, pull request reviews), GPT-5-Codex shows clear advantages: better bug detection, better reasoning about dependencies and context, better token and latency efficiency in many scenarios.
So, in short: Yes, Codex (GPT-5-Codex) is better than generic GPT-5 for software engineering tasks; but “better” depends heavily on the use case. For general language, creative work, or non-coding tasks, generic GPT-5 remains relevant.
Features: Codex CLI, API, IDE Extension, Cloud Tasks
GPT-5-Codex isn’t just a model; it comes with tooling designed to embed it into developers’ workflows.
Codex CLI
- The Codex CLI is a terminal/command-line interface tool, open-source (Rust-based) for speed and local performance.
- It can read, modify, and execute code in the working directory. Supports prompt inputs, image inputs (e.g., screenshots or diagrams), to-do tracking, and interactive modes of approval (e.g. “Read-Only”, “Approval Mode”, “Full Access”).
- It supports configuration via a ~/.codex/config.toml file, including support for Model Context Protocol (MCP) servers.
IDE Extension
- Available for Visual Studio Code and forks, Cursor, etc.
- Lets you preview diffs, open cloud tasks from the editor, review completed tasks, work between local and cloud contexts without losing state.
Codex Cloud / GitHub Integration
- Codex cloud tasks allow delegation of larger or more complex jobs, code review of pull requests, running tests in containers, attaching logs/screenshots to tasks or PRs.
- GitHub integration includes a review bot that can inspect dependency graphs, test correctness, and catch critical flaws across repositories.
API & Model Options
- Although Codex API access is being expanded, it is not universally available for all users yet. It is “available soon” for members using Codex via API key.
- Users can choose reasoning levels (e.g. low, medium, high) depending on complexity of the task, which influences how much “thinking time” the model spends.
Security, Safety, and Trust Features
When we’re talking about agentic coding (letting the AI modify, run, test, etc.), safety and trust are crucial.
- Approval Modes: Codex CLI supports different modes (auto, read-only, full access) to limit potential unwanted modifications or security risks.
- Network Access Control: For cloud tasks or agents, you can limit network access to trusted domains.
- Model Context Protocol (MCP): Used for external tool usage, memory management, and ensuring context is handled securely.
- Code Review & Test Integration: GPT-5-Codex doesn’t just write code; it’s trained to run tests, catch high-severity bugs, reason across dependencies and verify behavior. This lowers the risk of shipping flawed code.
Practical Use Cases & Examples
Here are several real-world developer workflows where GPT-5-Codex shines, or has already been demonstrated:
Large-scale Refactors
Teams working on long-lived codebases often need to refactor across many files, changing patterns, interfaces, or reorganizing architecture. GPT-5-Codex can carry out such refactors possibly for extended durations (e.g., 7+ hours) with tests, handle dependencies, and deliver working results.
Pull Request Reviews
Developers can tag PRs with @codex review (or similar triggers) and Codex will examine code, dependencies, test failures. It can suggest fixes or highlight critical issues before merging.
Front-end & UI work
Codex now supports image inputs (screenshots, wireframes), so it can reason about what’s visible (e.g. layout, visual bugs), suggest style changes, detect inconsistencies. This is useful in UI/UX work.
Interactive Local Edits via CLI
The CLI lets you work in your own folder/repo, ask Codex to read code, fix tests, navigate codebase, and make iterative changes. This reduces friction from context switching between tools.
Educational / Business / Team Use
Since Codex is included in various plans (Plus, Pro, Business, Enterprise, Edu), organizations and teams can adopt it for code review workflows, improving code quality, accelerating development, and mentoring.
Limitations & Trade-Offs
GPT-5-Codex is impressive, but it’s not Suitable. Here are some limitations and trade-offs to be aware of:
- Specialization vs. Generality: Because Codex is optimized for coding, its performance on non-coding tasks may lag behind general GPT-5. If your use case involves mixing creative writing, analysis, or domains outside software engineering, you might prefer generic models.
- Dependence on Test Suites: Many of its safety and correctness checks assume there are tests in place. Codebases without good test coverage may lead to less reliable results. Tests allow automatic validation; without them, human review remains essential.
- Long Tasks = More Time & Resources: For complex refactors or large changes, reasoning and compute time is longer; cloud charges, token usage, memory etc. These costs can add up. It’s also possible for the model to stall or misinterpret large codebases or complex interdependencies.
- Potential for Overhead & False Positives: Code reviews or automated suggestions might flag issues that are non-critical or stylistic, which could lead to extra work. False positives may reduce trust if too many.
- Rollout & Access Delays: Some features (e.g. API access, some plan tiers) are still being rolled out. Not all users may have immediate access to full GPT-5-Codex functionality.
GPT-5-Codex CLI vs GPT-5-Codex API vs Other Interfaces
It helps to understand the difference between using Codex via local CLI, via API, or via IDE / cloud.
- CLI (Local): Works locally, reads/modifies/runs code in your directories. suitable for developers who prefer staying in a terminal or local environment. Offers more control over codebase and privacy, lower latency for local operations. Approval modes help with safety.
- IDE Extension: Integrated into editors (like VS Code). Better context, ability to see visual diffs and previews, smoother transitions, easier for developers who like GUI + code. Great for real-time collaboration.
- Cloud / GitHub / API: Useful for heavy workloads, tasks that need server resources, cross-repo work, code review bots, continuous integration. Also useful for teams. But requires careful security, e.g., limiting network access, ensuring private repos are handled safely. API access is being expanded.
How GPT-5-Codex Compares to Other Coding Models
There are several competitors and sibling tools in the AI coding space: Claude Code (Anthropic), GitHub Copilot, Cursor, and more. Here’s how GPT-5-Codex stacks up:
- Competitor Benchmarks: GPT-5-Codex’s 74.5% success rate in SWE-bench is competitive with top peer models. It is also stronger than generic GPT-5 on refactor tasks.
- Tooling & Integration: The unified experience across CLI, IDE extension, cloud tasks, and code review gives Codex strong usability. Some competitors may be strong in one domain (e.g. Copilot in IDE suggestion), but Codex aims at a fuller stack.
- Agentic Autonomy: GPT-5-Codex’s ability to carry out long tasks with minimal supervision (e.g. long refactors, multi-hour testing and correction) is more advanced than many models that are more reactive.
- Token / Cost Efficiency: The substantial token savings on small tasks means lower cost for many day-to-day interactions, which is important for developers sensitive to usage and billing.
- Safety & Review: The improved code review capabilities and dependency reasoning are important distinguishing features.
Getting Started: How Developers Can Use GPT-5-Codex Today
If you’re a developer wanting to use GPT-5-Codex, here are practical steps:
Check Your Plan / Access
You’ll need a Codex-enabled plan (Plus, Pro, Edu, Team, Enterprise) for full access. API access is rolling out.
Install Codex CLI or IDE Extension
- CLI: Install via npm (npm install -g @openai/codex) or via Homebrew. Authenticate with your ChatGPT-account.
- IDE extension: For VS Code or compatible editor. Install and sync with cloud tasks if needed.
Learn the Modes & Approval Settings
Use “read only,” “approval,” or “full access” modes appropriately. Limit network / external tool access when security matters. Understand reasoning level settings.
Use Code Review Features
Use @codex review in pull requests, or enable automated reviews for repos. Add context like “focus on security” or “check dependency tree” to guide the review.
Test & Validate
For big changes, make sure you have good test coverage. Let Codex run tests, inspect output, and only accept changes after human review.
Monitor Cost / Token Usage
Watch usage especially on cloud tasks. Lightweight tasks will cost less, but long or large codebase tasks may accumulate compute usage. The new efficiency helps, but not indefinitely free.
Future Directions & What to Watch
Here are likely trends and areas where GPT-5-Codex and similar models will evolve, or where open questions remain:
- Better Generalization Outside Code: Bridging gaps so that coding-specialized models can still perform well across non-code tasks or mixed tasks.
- Stronger Privacy & On-Device Availability: More local / offline modes, better control of proprietary codebases, limiting data exposure to cloud.
- Improved Interpretability & Explainability: Not just code generation, but clearer explanations, reasoning logs, so developers can understand how decisions were reached, especially for bug fixes or refactors.
- Industry / Regulatory Standards: As AI code-generation becomes more embedded, there may be standards for safety, liability, and software quality.
- Better Test & Feedback Loops: More automatic test generation, dependency analysis, continuous feedback to improve model performance in production environments.
Conclusion
GPT-5-Codex is a major milestone for AI in software engineering. It combines the power of GPT-5’s general reasoning with focused improvements that make it significantly better for coding: refactoring, code reviews, long tasks, dependency reasoning, and cost efficiency. For developers, it means fewer friction points switching between tools, better assistance in large codebases, and more confidence in automated support.
However, it is not a silver bullet. Successful use depends on good test coverage, careful human oversight, thoughtful security settings, and realistic expectations. In many cases, generic GPT models may still be more flexible for non-coding tasks. But for teams and individuals centered around software development, GPT-5-Codex offers a powerful ally.
If you’re a developer, start experimenting with Codex CLI or the IDE extension, try out small refactors, test out reviews on pull requests, and evaluate how much it helps your workflow. If you’re part of a company, think about integrating GPT-5-Codex into your CI/CD pipeline, code review process, and internal developer tools—being early could offer competitive productivity gains.
Summary
| Feature | GPT-5-Codex |
| Success rate on SWE-bench | ~74.5% real-world coding tasks |
| Refactor success | ~51.3% up from ~33.9% |
| Token use for small tasks | ~93.7% fewer tokens than generic GPT-5 |
| Long-running tasks | Can operate >7 hours independently |
| Interfaces | Codex CLI, IDE extension, Cloud / GitHub integration |
